How Do Search Engines Work? Understanding the Components of Google SEO
Introduction
Search engines play a crucial role in our daily lives, helping us find information, products, and services with just a few clicks. But have you ever wondered how search engines work? In this article, we’ll delve into the inner workings of search engines and explore the key components of Google SEO.
In the vast landscape of the internet, Google stands as the undisputed search engine giant. Millions of queries are processed every second, leading users to a treasure trove of information. Have you ever wondered about the intricate details that go into creating a Google Search results page? Let’s dissect the anatomy of this virtual gateway to knowledge.
Search Bar:
At the very top lies the search bar, the gateway to a world of information. Users input their queries here, triggering a complex algorithm that scours the internet for relevant content.
Search Button:
A simple click on the magnifying glass or pressing “Enter” initiates the search process. Behind the scenes, Google’s algorithms work tirelessly to understand the user’s intent and deliver the most relevant results.
Search Results:
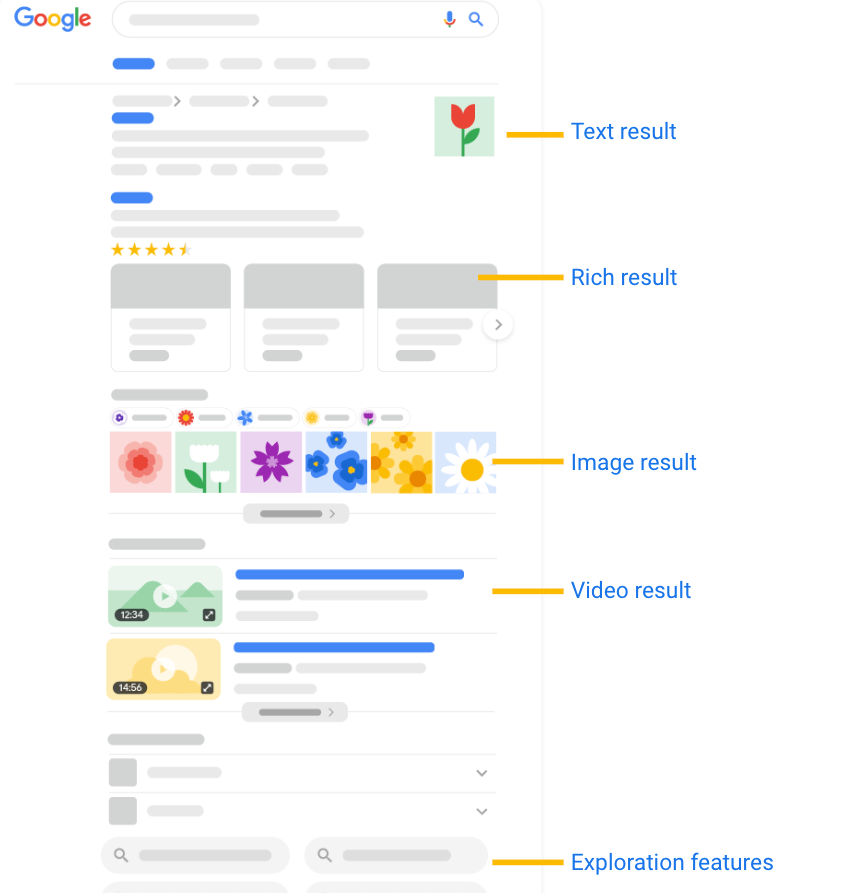
The core of the page is, of course, the search results. Typically presented in a list format, these results are a blend of organic and paid content. The organic results are algorithmically determined based on relevance, while paid results are advertisements targeting specific keywords.
Featured Snippets:
Featured snippets, also known as “position zero,” provide a concise answer to the user’s query at the very top of the results. Google extracts this information from authoritative sources to offer users a quick and direct response.
Knowledge Graph:
On the right side of the results page, you may find the Knowledge Graph. This visually appealing section provides a summary of information related to the search query, offering a snapshot of key details without requiring users to click through to other pages.
Related Searches:
Towards the bottom of the page, Google often includes a section of related searches. This assists users in refining their queries, helping them to explore additional topics or find more specific information.
Ads:
Interwoven with the organic search results are paid advertisements. These ads are strategically placed to blend in with the rest of the results, ensuring visibility without compromising the user experience.
Filter and Tools:
Located above the search results, users can find tools to refine their search further. This includes filters for time, type of content, and more. These tools empower users to tailor their search experience to suit their specific needs.
The Basics of Search Engines
At their core, search engines are complex algorithms designed to retrieve and rank relevant web pages in response to user queries. When you type a search term into a search engine, it scours the web for pages that match your query. But how does it determine which pages to show first?
Crawling and Indexing
To provide accurate and timely results, search engines rely on a process called crawling and indexing. Crawling involves the search engine’s bots, also known as spiders, visiting websites and following links to discover new pages. These bots analyze the content and structure of each page they encounter, storing the information in a vast database called an index.
Indexing is the process of organizing the information gathered during crawling. Search engines use complex algorithms to determine the relevance and quality of each page, considering factors such as keyword usage, backlinks, and user engagement metrics. The index is constantly updated as new pages are discovered and existing ones are reevaluated.
Ranking and Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Once a user submits a search query, the search engine’s ranking algorithm comes into play. The algorithm analyzes the indexed pages that match the query and assigns them a rank based on various factors. This is where Search Engine Optimization (SEO) comes into play.
SEO refers to the practice of optimizing web pages to improve their visibility and ranking in search engine results. While Google’s ranking algorithm comprises hundreds of factors, there are a few key elements to keep in mind:
1. Relevant Content
Search engines prioritize pages that provide valuable and relevant content to users. Creating high-quality, informative, and engaging content that aligns with user intent is crucial for SEO success.
2. Keywords and Semantic Variations
Keywords play a significant role in SEO, but it’s essential to use them naturally and not overstuff your content. Including relevant keywords and their semantic variations helps search engines understand the context and relevance of your content.
3. Backlinks
Backlinks are links from other websites that point to your site. They serve as a vote of confidence and can significantly impact your search engine rankings. Building high-quality backlinks from reputable sources is an important aspect of SEO.
4. User Experience
Search engines consider user experience signals, such as page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and ease of navigation. Optimizing your website for a seamless user experience can positively impact your rankings.
5. Technical Optimization
Technical aspects, such as proper website structure, meta tags, XML sitemaps, and schema markup, also contribute to SEO. Ensuring your website is technically sound and follows best practices helps search engines understand and index your content effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding how search engines work and the components of Google SEO can help you create a strong online presence. By optimizing your web pages with relevant content, keywords, backlinks, and a focus on user experience, you can improve your rankings and drive organic traffic to your site. Remember, SEO is an ongoing process, and staying up-to-date with the latest industry trends and algorithm changes is key to success.

